Insurance companies need to think of technology and talent investments as intertwined facets of their business.
Insurance industry outlook key takeaways
AI works in tandem with machine learning, allowing insurers to connect everything insurance to smart devices.
Insurers should develop solutions for processes found in modern insurance technology stacks.
Unleashing the potential of automation requires insurers to make strategic investments in their technology and people. Artificial intelligence and machine learning specifically can provide flexibility that allows insurers to innovate and transform faster in key business areas such as distribution, underwriting, policy services or claims management, while attracting and retaining talent by providing more meaningful work. Insurance companies that want to thrive in the future need to think of technology and talent investments as intertwined, symbiotic facets of their business.
More and more insurers are leveraging AI to meet changing customer demands. Insurers are also using AI to create automated workflows, leveraging data and algorithms to automate risk management tasks like recognizing underwriting risks and detecting fraud more effectively. Some insurers, for instance, are leveraging AI’s natural language processing and advanced analytics capabilities to extract pertinent risk information from emails, enabling them to identify underwriting risks and optimize the customer experience. By integrating insights from advanced data sources such as smart devices, wearables, telematics, and other connected technologies, insurers can create a single source of truth to deliver a personalized customer experience while optimizing internal business value.
AI works in tandem with machine learning, allowing insurers to expand the insurance ecosystem by connecting everything insurance to IoT and smart devices. This can improve decision making, boost productivity, and reduce the frequency and severity of allocated loss adjustment expenses in claims, for example. Insurance companies can achieve a reduction in insurance claims and create a sustainable, predictive model to better forecast claims reserves and outcomes.
For example, attended bots and virtual agents can assist customers seeking personalized insurance products using ML algorithms that review customer profiles and recommend personalized products. Some insurers are using messaging applications as part of their communication framework to resolve claim inquiries and provide status updates.
Insurers are also starting to explore digital ledger systems like blockchain to reduce human error, hours of paperwork and manual processes, providing a clearer record of events in chronological order while safeguarding and storing sensitive information. For example, blockchain technology supports safer and faster proof of insurance, allowing customers to verify their information more quickly.
AI and ML techniques can also have profound applications across an enterprise that continuously looks to technology to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of processes. Here are three examples:
- Claims departments can leverage AI-enabled tools like intelligent automation to perform claims processing tasks through proactive management, improving operational efficiencies and claims settlements.
- Risk management can use ML to predict premiums and losses, premium leakage and risk appetite with greater accuracy, enhancing insurers’ understanding of their risks and their ability to make informed business decisions.
- Fraud prevention can leverage ML algorithms to process structured and unstructured data, enabling insurers to identify fraud faster and prevent it more effectively.
Addressing talent gaps
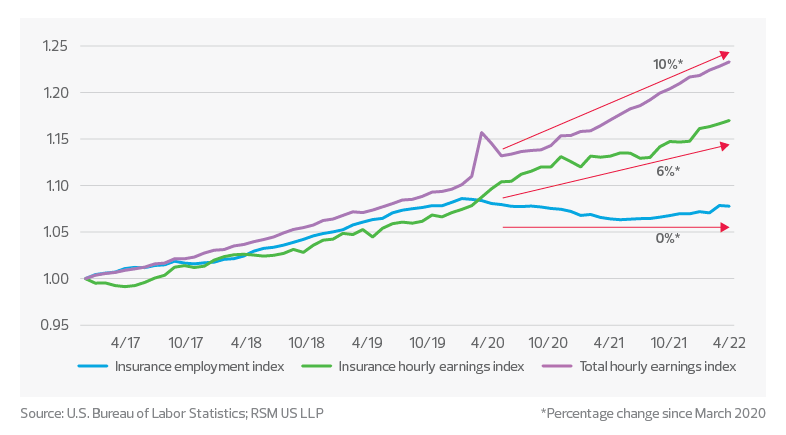
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, there were 4.2 million quits in June 2022. Due to the ongoing talent shortage, coupled with the aging workforce and baby boomer retirements, insurers are rushing toward digitization and emerging technologies to expand their capabilities and services. In 2022, the data shows continued stagnant employment growth despite higher wages, suggesting workplace transformation. Carriers have been leveraging AI in business processes that are ripe for automation, which can result in the elimination of repetitive administrative tasks.
However, the skilled insurance workers who remain on the job are not experiencing wage growth to the same extent as the broader economy, which will pose continued retention and recruiting challenges for insurance companies. To attract and retain talent, some insurers have developed rotational programs, innovation hubs, or robust mentorship programs in which employees can gain exposure across functions and expand their skills and business acumen to create a diversity of experience. In this tight labor economy, it is more critical than ever for insurance companies to build and maintain a strong talent bench by investing in the employee experience at all levels.
Average hourly earnings have significant outpaced employment in the insurance sector since the start of the pandemic, but wages are still not keeping up with the overall economy
Considerations for the future
We expect more and more insurers to use cognitive analytics to access unstructured data that can help reduce biases in decision making and enable greater visibility into an organization's true risk exposure. We also anticipate AI applications and intelligent assistants will become commonplace across insurance companies’ technology stack, enabling insurance professionals to make more informed decisions in managing risk across the business.
Historically, companies have made significant investments in data foundation and transformation initiatives to extract data from legacy IT systems and put it to use. When implementing AI into business processes, insurance companies should focus on developing solutions for processes found in modern insurance technology stacks, where data recency is critical and legacy data is less relevant. Organizations should not let legacy issues define their AI strategy.
In the effort to develop a holistic AI strategy, insurers might consider working with a third party that can provide a clear assessment of how to increase revenues and accuracy and reduce operational costs, and recommend, implement, and monitor solutions for scalability and continuous improvement.


